






InUrSkn is more than just a skin a hair and body clinic. It is Dr. Sejal's promise of providing minimal intervention patient care which is holistic, personalized and humane.













Psoriasis is a chronic, cyclic disorder manifesting in red, itchy lesions with silvery flakes due to rapid skin cell growth, often affecting nails too. It may subside for periods, only to recur, notably on lower back, elbows, knees, and scalp. Around 25% of cases exhibit psoriatic arthritis. Triggered by factors like stress and weather changes, its underlying cause links to immune system malfunction. Management involves oral/topical medications and light therapies such as Excimer Laser, aimed at controlling outbreaks and alleviating symptoms.
Read More
Vitiligo, an autoimmune disorder, results from the immune system attacking skin melanocytes, leading to white patches. Onset is typically between 30-50, with unpredictable progression. Triggers include stress and skin trauma. Treatment options vary based on severity.
Read More
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis in children, is a chronic yet manageable skin condition characterized by itchy, red rashes, often with oozing fluid and dry, cracked skin. Genetic variations affect moisture retention. Management includes regular moisturizing, avoiding irritants, prescribed medications, and lifestyle adjustments.
Read More
Rosacea, often recognized by flushed red cheeks, presents as painful boils or bumps on the face, mainly the cheeks or nose, alongside flushing. While its exact cause remains unknown, it’s speculated to arise from hereditary, environmental, and immune system factors. Often misdiagnosed as other skin ailments like acne, Rosacea may be accompanied by eye changes like watering or burning. Common triggers include hot drinks, spicy foods, and emotional changes. Treatment primarily involves topical and oral medications to modulate blood flow and reduce bumps, aiding in symptom management.
Read More
Lichen Planus, a chronic autoimmune condition, affects skin, mucosa, hair, and nails, often in middle-aged adults, causing small, flat, purplish lesions. Management involves medications to control symptoms and prevent complications.
Read More
Hives, or urticaria, result from allergic reactions, causing itchy raised bumps with red or pink appearance. Triggers include foods, insect bites, medications, or sun exposure. Chronic hives may signal underlying conditions, managed with antihistamines or moisturizing emollients.
Read More
Lupus is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly targets one’s own tissues and organs, affecting multiple body systems including skin, hair, kidneys, joints, and heart, predominantly in females aged 20-40. Manifesting in three main types—acute, subacute, and chronic lupus—it can present varied symptoms like skin lesions, hair fall, and joint pain. Triggered by factors like sunlight, certain medications, or infections, diagnosis often involves specific blood tests and imaging, with treatment entailing oral medications and sun protection.
Read More

Chronic skin conditions are persistent ailments that affect the integumentary system (skin, hair, nails, and mucous membranes), often lasting for many years or a lifetime. Unlike acute conditions which may resolve with time or treatment, chronic skin issues often require ongoing management to control symptoms, minimize flare-ups, and maintain the individual’s quality of life. Common chronic skin conditions include eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, vitiligo, lichen planus, and chronic hives (urticaria).
These conditions may exhibit a range of symptoms such as inflammation, itching, redness, scaling, pigmentation changes, and sometimes pain. The exact cause of many chronic skin conditions remains unclear, but they often have genetic, immunological, and environmental triggers. Moreover, they may be associated with other systemic conditions or have comorbidities like psoriatic arthritis in the case of psoriasis or eye issues in the case of rosacea.
Management of chronic skin conditions may encompass topical and oral medications, light therapy, lifestyle modifications, and occasionally surgical interventions. Although they are typically not curable, appropriate medical care and lifestyle adjustments can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve the appearance of the skin. It’s crucial for individuals with chronic skin conditions to work closely with dermatologists to tailor a management plan that addresses their specific needs and enhances their overall wellbeing.

Dr. Sejal understand that treating a chronic condition is not just about reducing the symptoms but about improving the quality of life of the patient. A lot of chornic skin conditions become a source of social anxiety and need cosmetic resolutions also. Dr. Sejal brings her 15+ years of experience in domains of both dermatology and cosmetology into the treatment and care of chronic skin conditions. She offers a holistic approach to managing chronic skin conditions which include the below:
1. Detailed Assessment and Diagnosis
2. Patient Education
3. Personalized Treatment Plans
4. Lifestyle Recommendations
5. Long-term Monitoring and Follow-up
6. Emotional and Psychological Support
7. Coordination with Other Healthcare Professionals
8. Encouragement of Patient Self-management
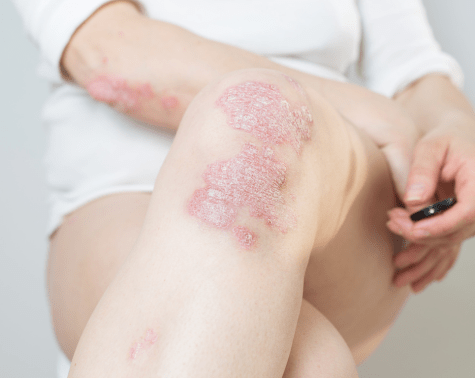
Psoriasis is chronic (long lasting) condition which can be controlled but not cured. It presents as multiple itchy red lesions with silvery white flakes. This formation of skin flakes is because of a rapid growth of skin cells. Often nails are also found to be affected.
Psoriasis is a cyclical disporder in which the condition may flare up for a few weeks or months and then go into remission, only to return again.
Psoriasis is commonly seen on lower back, elbow, knees, palms, soles, scalp etc. It can be localised or generalised.
In about 25% of the cases it is accompanied by psoriatic arthritis.
Common symptoms of psoriasis include:
Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
Small scaling spots
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed or itch
Itching, burning or soreness
Thickened, pitted or ridged nails
Swollen and stiff joints
Psoriasis is a problem caused by the malfunctioning of the immune system. The exact reason for such a malfunction remains unknown.
People who are known to be at risk of getting psoriasis are as below:
– Family History of Psoriasis
– High Levels of Stress
– Smoking
Psoriasis is aggravated by the following factors:
Stress
Dry weather
Sudden weather changes
Sore throat
Certain Medications
Mild trauma or injury can trigger new patches
Control on these factors can help reduce psoriasis outbreaks
Psoriasis lesions are treated with the help of oral and topical medications. In addition they can be treated by light therapy. At InUrSKn we offer the below light treatment for psoriasis:
Excimer Laser
Common triggers include stress, certain medications, skin injuries, infections, and weather changes.
Some individuals find relief by reducing alcohol, gluten, or nightshades, though results vary.
Yes, types include Plaque, Guttate, Inverse, Pustular, and Erythrodermic psoriasis.
No, psoriasis is not contagious and cannot spread between individuals.
No, it can also affect nails and joints, a condition known as psoriatic arthritis.
Sunlight can be beneficial in moderation, but sunburn can trigger flare-ups.
Yes, it can be associated with heart disease, diabetes, and other autoimmune disorders.
Stress can trigger flare-ups and managing stress can potentially reduce symptoms.
There’s no cure, but treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
They have different appearances, and a dermatologist can provide an accurate diagnosis.

It is an autoimmune condition where body’s immune system attacks the melanocytes in the skin which are the cells responsible for producing melanin. Melanin is what provides colour to our skin. Destruction of melanocytes ensure that melanin production is stopped in the area in question and the skin turns ‘white’. Vitiligo is not a contagious disease. It can occur at any age, but is commonly seen between 30- 50 years of age. It presents as well defined white or discoloured patches on any part of the body commonly seen on hands, legs and face.
Vitiligo can be localized (restricted to few areas of the body)
Generalised( most of the areas are involved)
Universal(entire body is involved)
Hair can also get affected and become white.
Also unfortunately the course of this condition is unpredictable and hence there can be a rapid increase or decrease in vitiligo lesions.
While the exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, it is known to be hereditary. Also Vitiligo is an autoimmune disease, that is it is your body’s own immune system which malfunctions and attacks healthy cells of the body.
Vitiligo can be triggered by Stress and by any trauma to the skin. It is also known to become dominant after the body has undergone substantial stress like undergoing surgeries. Lastly Vitiligo is known to be seen in association with other conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders and other autoimmune diseases.
As vitiligo does not have known causes besides it being hereditary, there are very few things that can be done to prevent its flare up. One of the most effective things Dr. Sejal prescribes is ensuring that one does not undertake undue stress. Any strategy that works to help a person destress from exercise to meditation to simply watching television works.
Also there are poor associations between dietary intake and other factors like environmental exposure and vitiligo and hence controlling these aspects also does not help much.
There are largely three strategies followed for vitiligo patients:
1. Camouflage
This is suitable for mild and localized cases in which small depigmented patches appear on visible areas of the body. In this case these areas are covered with temporary or semi-permanent makeup pigment to blend with the surrounding area. Treatments like microblading are suitable for covering such spots for a long lasting pigment colouration.
2. Regaining Natural Melanin
This is also suitable for mild and localized cases for repigmenting the areas in question. This uses mechanisms like excimer laser and other UV devices to stimulate melanin generation in the affected area.
3. Removing pigment from other areas
For widespread and severe cases, this may be a workable strategy where the areas with pigment are treated with topical medications to remove the pigment in those areas to achieve an even skin colour across the affected area. This strategy has to be considered with due seriousness before proceeding with the same and the treating dermatologist has to be very careful.
No, vitiligo is not contagious and there’s no need to avoid contact with affected individuals.
Yes, vitiligo affects individuals of all ethnicities and races. It may be more noticeable on darker skin, but it occurs equally.
No, vitiligo is an autoimmune condition unrelated to dietary or lifestyle choices.
No, untreated vitiligo may progress. It’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for treatment options as soon as it’s diagnosed.
Yes, treatments like topical and oral medications, as well as light therapies that stimulate melanin production, can help manage vitiligo.
Sun exposure does not typically affect vitiligo, but protecting the skin from sunburn and excessive sun exposure is advisable. Other environmental conditions generally do not affect vitiligo.
No, vitiligo and skin cancer are unrelated conditions, although individuals with vitiligo can develop skin cancer like anyone else.
No known natural or herbal remedies have been proven effective for vitiligo. It’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for treatment.
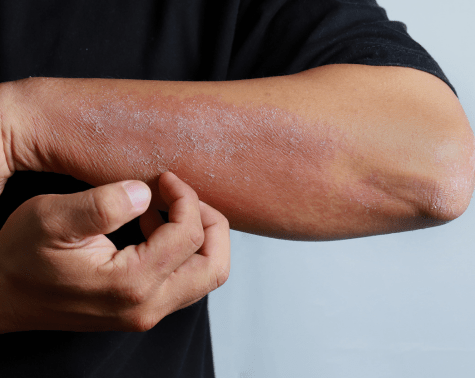
Eczema is a chronic (long lasting) condition that is controllable but unfortunately not curable. It presents as itchy red rashes, which ooze liquid and accompanied by cracked and dry skin. It can occur at any age. When occurring in children, it is called as atopic dermatitis. Eczema can occur on any part of the body. It is non contagious.
Symptoms of eczema include the below:
Dry skin
Itching
Red to brownish-gray patches
Small, raised bumps which may have fluid.
Thickened, cracked, scaly skin
Raw skin from scratching
Eczema mainly occurs on areas like, hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, inside the bend of the elbows and knees. In infants, the face and scalp can also be covered.
Eczema is mainly genetic in nature. Meaning there is a variation in a gene which causes the skin to lose its ability to retain moisture and dry out quickly. This in turn causes the skin to be affected by allergens and irritants and also environemntal factors.
Prevention of new eczema patches and control of the same can be done by :
– Using a moisturizer regularly, ensuring that the skin is always well hydrated.
– Avoiding aggravating factors like allergens, irrutants or stress etc.
– Ensuring that the skin does not dry out due to exposure to hot water or dry weather.
– Avoiding any physical abrasion to the skin
Eczema is laregly treated with oral and topical medication in combination with appropriate lifestyle and habit changes.
Yes, certain food allergies can trigger eczema flare-ups, particularly in children. Common triggers include eggs, dairy, nuts, and soy.
Yes, dry or cold climates can worsen eczema symptoms as they can dry out the skin further. Humid climates may provide some relief.
Yes, stress is known to trigger or worsen eczema flare-ups in some individuals.
Yes, eczema is often associated with other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever.
Eczema doesn’t spread like an infection, but it can appear on different parts of the body at different times.
Currently, there’s no permanent cure for eczema, but treatments can effectively manage and alleviate symptoms.
It’s recommended to moisturize the skin at least twice a day, or more often if necessary to keep the skin hydrated.
Over-the-counter creams may help with mild eczema, but it’s advisable to consult with a dermatologist for persistent or severe cases.
Yes, scratching can worsen eczema and potentially cause infection if the skin is broken.
Some individuals find relief by eliminating foods that trigger allergies, though it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes.
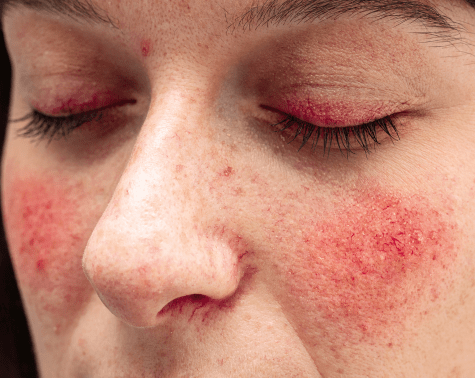
Flushed Red Cheeks are called as Rosacea. It is different from healthy red cheeks. It is seen as red painful boils or bumps seen on cheeks or nose. It is accompanied by flushing. Some of the cases are accompanied by changes in the eye like watering or burning of eyes.
Rosacea is often wrongly diagnosed as otehr skin ailments like acne.
The primary cause of rosacea is unknown. It is postulated to be a combination of heriditary, environmental and iimmune system related causes.
People who fall in the below demographics are more likely to develop rosacea:
1. Females
2. Light Skinned
3. Over the age of 30
4. Engage in Smoking
5. Have family history of Rosacea
Rosacea can be triggered or aggravated by the following:
– Hot Drinks
– Spicy Foods
– Alcohol Consumption
– Hot Weather
– Exercise
– Emotional Changes
– Certain medications that affect vascular functioning
– Some topical skin and hair products
Avoiding these stimuli can help avoid rosacea flare ups.
Rosacea is mainly treated with topical and oral medications which module blood flow and also medications that help reduce bumps and pimples.
No, there isn’t a cure for rosacea, but with proper treatment and management, its symptoms can be controlled.
No, rosacea is not a contagious condition.
Yes, in severe cases, rosacea can cause skin to thicken, especially around the nose.
Yes, ocular rosacea can cause redness, irritation, and swollen eyelids.
Laser treatment can be effective in reducing redness and visible blood vessels associated with rosacea.
Yes, sun exposure can trigger or worsen rosacea flare-ups. Wearing sunscreen and protective clothing is advisable.
Some studies suggest a connection between gastrointestinal disorders like SIBO and rosacea. Further consultation with a healthcare provider is advisable.
Individuals with rosacea should avoid harsh or abrasive skincare products, as well as those containing alcohol, witch hazel, or fragrances.
Rosacea can worsen over time without treatment, though individuals may experience periods of remission.
Over time, untreated rosacea can lead to permanent changes such as skin thickening or visible blood vessels.
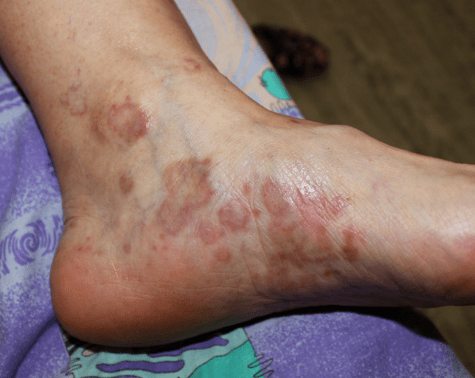
It is a chronic condition of the skin, mucosa, hair follicles and nails. It can occur in any age group but is more commonly seen in middle aged adults.
It presents as small, flat topped, purplish lesions present on wrists, legs, back, back of hands and sometimes genitals. Inside the mouth they are seen as whitish lesions and ulcers. There are thicker lesions on palm and soles.
Nails are also affected in the form of thick ridges and destruction of nails. Hair loss can occur which can be scarring or non-scarring in presentation.
Lichen Planus is an autoimmune condition in which case the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells in the skin and mucosa.
Lichen Planus is seen to mainly occur in middle agen people. The causative factors can include the below:
– Family History of Lichen Planus
– Viral Infection like Hepatitis C
– Exposure to allergens and irritants
– Sunlight Exposure
Certain medications and vaccines are also known to trigger lichen planus like pain killers and arthritis medications. Also some dental treatments involving mercury can trigger lichen planus lesions.
Lastly stress can be a factor in triggering lichen planus.
Lichen planus can cause the below complications:
– Skin lesions heal and leave behind long lasting marks
– Ulcers in the mouth are painful and difficult to eat.
– Rarely oral lesions when left untreated can lead to cancer.
– For mild cases: oral anti-histaminics and topical creams
– For moderate to severe cases: oral medications in the form of steroids, immune modulators, and retinoids.
– When caused by certain medicines, discontinuation of those drugs helps.
– Hair loss can be treated with oral medication and topical solutions
– For marks and scars along with topical creams, pigmentation treatment in the form of lasers or peel also help.
No, Lichen Planus is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
Yes, although it’s more common in middle-aged adults, it can occur in children.
There is no cure for Lichen Planus, but treatments can help manage symptoms and alleviate discomfort.
Yes, the lesions from Lichen Planus can heal and leave behind long-lasting marks or scars.
Yes, certain medications, stress, and exposure to allergens and irritants can trigger flare-ups.
Yes, it can affect the skin, mucous membranes, nails, and hair follicles.
Lichen Planus has been associated with Hepatitis C infection in some cases.
Yes, it can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions, making correct diagnosis crucial for appropriate treatment.
Treatments may include topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, immune modulators, and retinoids, depending on the severity of the condition.
Yes, Lichen Planus can recur, and it may come and go over many years.
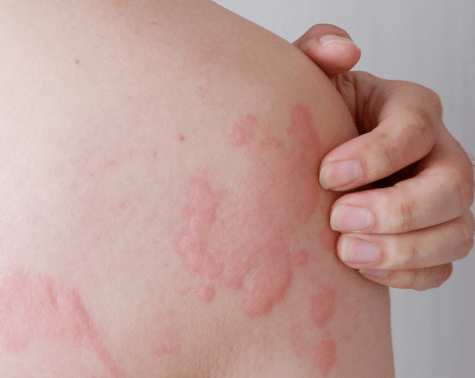
Hives are nothing but an allergic reaction which presents as itchy raised bumps. These bumps can occur on any part of the body. They are usually red, pink, or flesh-colored, and sometimes they sting or hurt.
Allergic reactions occur when the body begins to release histamines into blood. Histamines are chemicals the body produces in an attempt to defend itself against infections and any foreign body. In some people, these histamines can cause swelling, itching etc.
Most people suffer from hives as a temporary condition in which case the lesions go away by themselves or after using anti-allergy medication. But in some cases the hives can be chronic condition accompanied by other issues.
The different reason for allergic reactions that lead to hives are:
Certain Foods
Insect bites
Certain Medicines
Anxiety
Cold temperature
Exercise
Sun exposure
Unfortunately in most of the cases it is not possible to find the exact cause.
If you suffer from chronic case of hives, then you may have an underlying complication like:
Diabetes
Lupus
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Thyroid disorder
celiac disease
Hives being an allergic reaction can only be prevented by preventing any interaction with the causative factor. However often it is very difficult to determine the exact causative factor. The symptomatic treatment for hives includes use of antihistamines. To bring about immediate relief a doctor may prescribe a moisturizing emollient.
The common symptoms include itchy, red or flesh-colored bumps or welts on the skin, which may sting or hurt.
Acute hives may last less than six weeks, while chronic hives can last more than six weeks, sometimes even years.
No, hives are not contagious and cannot spread from person to person.
There is no cure for chronic hives, but symptoms can be managed with medications and lifestyle adjustments.
Hives are diagnosed based on a physical examination and your medical history. Further tests might be necessary if chronic hives are suspected.
Antihistamines are the most common medication used to treat hives, and in severe cases, corticosteroids or epinephrine might be used.
Yes, stress can be a trigger for hives in some individuals.
It’s advisable to see a doctor if hives persist, are severe, or if you experience other symptoms like difficulty breathing.
Yes, chronic hives can sometimes be a sign of underlying conditions such as autoimmune diseases.
Cool compresses or baths, wearing loose-fitting clothes, and avoiding irritants can help alleviate symptoms, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for persistent or severe cases.

It is an autoimmune condition where your body’s immune system attacks your own tissues and organs. It can affect multiple system of the body causing inflammation of skin, hair, kidneys, joints, blood vessels, brain and heart. Lupus occurs commonly between 20- 40 years in females.
Cutaneous Lupus: Lupus can present in 3 main types.
1. Acute cutaneous Lupus: Acute lupus almost always progresses to systemic involvement. Hence acute lupus should be closely monitored
2. Subacute lupus
3. Chronic lupus
Subacute and chronic usually are limited to skin involvement
Lupus is an autoimmune condition that has the below trigger or causative factors:
– Hereditary
– Genetic predisposition
– Triggering factors:
– Sunlight
– Certain medicines like blood pressure medicines, anti-seizure medicines etc.
– Certain infections
Symptoms and signs to watch out for in Lupus:
– Skin lesions present as itchy, red patches on cheeks and nose (butterfly rash)
– Subacute type presents as circular red lesions on sun exposed areas.
– Chronic type leaves behind scars and discoloration on face, scalp and ears.
– Diffuse hair fall can occur
– Scarring of hair follicles leads to patches of hair loss
– Hands turn blue on exposure to cold
– Other symptoms include joint pain, headache, shortness of breath, chest pain
– Can lead to pregnancy complications when the disease is active
– Specific blood tests like ANA confirm the diagnosis
– Imaging tests like x ray, ECG may be needed to confirm
– Sun protection is the most important to prevent flare ups.
– Oral medications like non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, immune suppressants Etc.
– De stressing exercises
Diagnosis may include a thorough examination by a healthcare provider, discussing symptoms and medical history, along with specific blood tests, like Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) test, and imaging tests.
Yes, besides Cutaneous Lupus, there is Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), which is more severe and affects many organs, and Drug-induced Lupus, triggered by certain medications.
No, lupus is not considered rare, although its prevalence can vary among different populations and regions.
It can be, especially if major organs are affected or complications arise. However, with proper management, many individuals with lupus can maintain a good quality of life.
Yes, complications may include kidney damage, heart and lung issues, or neurological problems, among others, which can significantly impact a person’s health.
Currently, there is no cure for lupus, but its symptoms and complications can often be managed with medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Besides medical treatment, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding sun exposure, managing stress, exercising regularly, and avoiding known triggers can help manage symptoms.
Although the exact cause is unclear, individuals with a family history of lupus or other autoimmune diseases may be at a higher risk.
Yes, lupus can cause complications in pregnancy. It’s essential for women with lupus to consult with healthcare providers when planning for pregnancy.
Generally, yes, but it’s essential to consult with healthcare providers to determine which vaccinations are safe and recommended.


MD, DNB - Dermatology & Venereology
Dr. Sejal has dual degrees of MD and DNB in Dermatology and Venereology. She has worked with some of the senior most doctors in the largest government and private hospitals for more than 15 years. Over these years at InUrSKn, she has treated thousands of patients for a variety of conditions and needs across dermatology, venereology, cosmetology and trichology domains.
Dr. Sejal believes in a minimum intervention approach to health and believes that educating and empowering the patient is the key to good health.
Every patient at InUrSkn is seen personally by Dr. Sejal without any time limit, where she discusses the patient’s concern in detail along with understanding the history of their health and carrying out a personal examination.
At InUrSkn we belive that all patient care must be
– Holistic
– Personalized
– Humane
– Minimal
That is Dr. Sejal and Team live by the philospohy to never prescribe medications or procedures that may not be required and while approaching a concern Dr. Sejal ensures that a detailed history and context is understood by her. Medical tests are prescribed by Dr. Sejal when she believes that there is more to the concern which needs to be addressed and only then the patient can truly benefit.
Multiple spacious procedure rooms
Full-fledged operation theatre
In-house laboratory
Latest technology
100+ Skin, Hair & Body Procedures offered
Frequent disinfection of all clinic spaces with UVC light and WHO-approved chemicals
Large waiting and treatment areas to ensure social distancing
Regular health checks for all patients and staff
Safer than salons, chain-clinics & hospitals
PPEs for patients and staff
Personal attention from Dr. Sejal Saheta (MD, DNB) - with 15+ years of experience
CIDESCO-certified aestheticians with minimum 3 years work experience
500+ Positive Reviews on Practo and Google
5000+ Patients treated last year alone
8000+ Procedures completed
| Prices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Procedure | ||
| In Clinic Consultation with Dr. Sejal | ||
| In Clinic Consultation with Dr. Sejal | ₹1100 | |
| Online Consultation with Dr. Sejal | ||
| Online Consultation with Dr. Sejal | ₹900 | |
Pricing (Inclusive of taxes)


Triggers can vary widely among different chronic skin conditions and individuals, common ones include stress, allergens, irritants, infections, hormonal changes, and genetic factors.
Most chronic skin conditions are not curable but can be managed effectively with the right treatment plan to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Certain foods may trigger or worsen symptoms in some individuals. A dermatologist might suggest an elimination diet to identify potential food triggers.
Dermatologists are the primary specialists for treating chronic skin conditions, though in cases of associated comorbidities, other specialists might be involved.
Stress can exacerbate symptoms of chronic skin conditions as it may trigger an immune system response that worsens inflammation.
Typically, chronic skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea are not contagious, but it’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Treatments may include topical creams, oral medications, light therapy, immunosuppressive drugs, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes surgical interventions.
Over-the-counter creams, prescription ointments, and avoiding known irritants can help manage itchiness. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Prevalence and severity of chronic skin conditions can vary across different age groups and genders, often influenced by genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
Yes, weather changes can affect chronic skin conditions. Cold, dry weather may worsen symptoms, while warmer, humid climates might offer relief for some individuals.
Yes, discomfort and itchiness from chronic skin conditions can interfere with sleep, and poor sleep may, in turn, worsen skin symptoms.
Smoking and alcohol can worsen symptoms of many chronic skin conditions due to their effects on the immune system and blood vessels.
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with healthcare providers can ensure that the treatment plan remains effective and adjusts to any changes in the condition.
Yes, dealing with persistent symptoms and physical discomfort can lead to anxiety, depression, or self-esteem issues, emphasizing the importance of psychological support in management plans.
Effectiveness can vary greatly among individuals. It’s important to discuss any alternative treatments with a healthcare provider to ensure they won’t interfere with existing treatment plans or worsen the condition.

Ready to book an appointment?
BOOK

Want to talk about your needs ?
MAKE AN enquiry
